The circle
If you take a piece of string and secure one end, then take the other end and
stretch it out and move it about 360 degrees you’ll have a circle. This means
all points on the edge of the circle are an equidistant from a fixed point (the
centre)
The other option is to think about the circle in terms of two stacked cones.
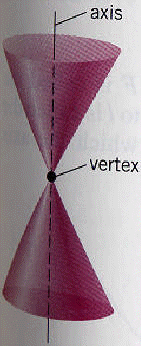
Take a horizontal cut, and it is the circle
The point P represents any point along the edge of the circle.
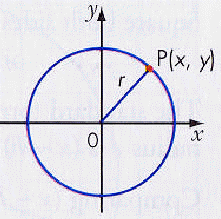
The length r, is equidistant from the centre to any point on the edge of the
circle.
The equation is for a circle is r 2 = x 2 + y 2.
This is the standard form of the equation, which is centered at the origin.
For circles not centered at the origin:
(x + h) 2 + (y - k) 2 = r 2, where h & k are
the co-ordinates of the origin
Example 1
What is the equation of a circle (centred at the origin) with a radius of 5?
Since r = 5, we substitute that into the equation
x 2 + y 2 = (5) 2
x 2 + y 2 = 25
Example 2
Write an equation of a circle with a radius of 4, and a centre @ (3,-1). State
the domain and range of the circle.
Using the equation (x + h) 2 + (y - k) 2 = r 2,
the radius 4, and the centre (3,-1)
(x - 3) 2 + (y - (-1)) 2 = 4 2
(x - 3) 2 + (y +1) 2 = 16 2
Domain : { x | -1 < x < 7; x
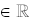 } }
Range : { y | -5 < y < 3; y
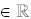 } }
Example 3
What is the equation of the circle in standard form, with centre at (-2,3)
and through the
point P(4,1)
Draw a picture to assist in the process.
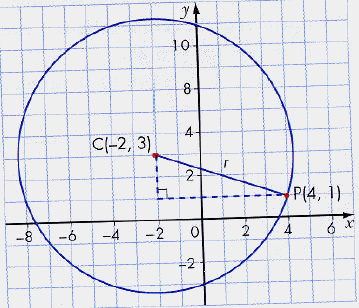
Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we can find the length of the radius.
r 2 = (4 - (-2)) 2 + (1 - 3) 2
r 2 = 36 + 4
r 2 = 40
Since we know the centre, the equation is (x + 2) 2 + (y - 3) 2
= 40
|